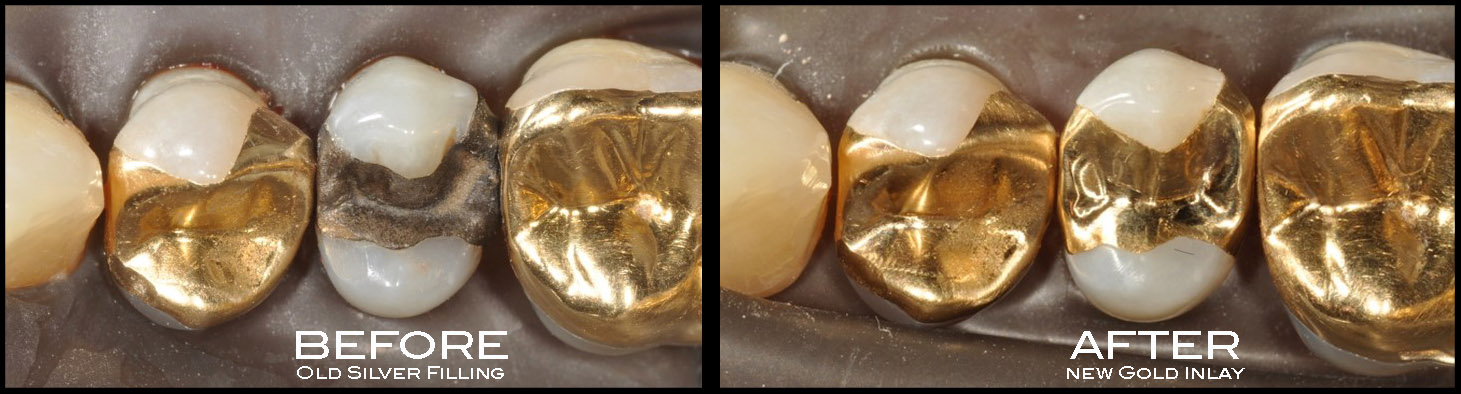
Gold Restorations
Dr. Chin is a member of a R. V. Tucker Gold Study Club. Each month Dr. Chin hones her clinical dental skills by perfecting the preparation of gold restorations. The study club consists of about twelve practicing dentists who meet monthly at the University Of Washington School Of Dentistry under the mentorship of a dentist who has been practicing the Tucker technique for over 30 years.
ADVANTAGES OF USING GOLD TO RESTORE POSTERIOR TEETH (from the R.V. Tucker website)
1. Gold will not oxidize and discolor the teeth.
2. Fragile areas of tooth structure remaining can be protected by covering them with a thin layer of gold. Gold will not fracture even when it is thin.
3. The cast gold restoration will not fracture in the isthmus (center area of teeth) or other areas.
4. The margins at the junction of the tooth and gold are nearly imperceptible if handled properly, and will not be so likely to harbor plaque, and consistently should contribute to better tissue health.
5. Contact areas can be placed and polished for ease in the use of dental floss, thus promoting better tissue health.
6. Gold can be polished and finished to a higher degree than other materials.
7. Gold castings such as 7/8 modified full crowns or conventional full crowns can be used to “bind the tooth together” and prevent tooth fracture, or relieve sensitivity from incipient tooth fractures.
8. The normal tooth anatomy can be more nearly reproduced with a casting.
9. Cast gold wears more nearly the same as tooth structure and does not produce sub-marginal surface. Precise fitting castings will support the marginal enamel rods which prevents chipping and fracturing at the cavo-surface margins and minimizes the possibility of marginal leakage and bacterial invasion.
10. Gold castings have a favorable coefficient of expansion with tooth structure.
11. Well placed gold casting will last much longer than other filling materials used today.
12. The sensory acceptance of gold by the tongue and the feel during mastication (chewing) is enhanced by the smoothness and anatomical replication of the missing tooth structure.